February 22, 2016
Input Prices
Domestic resource prices
-wages (75% of all business costs)
-capitol cost
-raw materials (commodity prices)
Foreign resources prices
-strong $ = low foreign resource price
-weak $ = higher foreign resource prices
Market power
-increase in resource prices = SRAS ß
-decrease in resource prices = SRAS à
Productivity
Total output/total inputs = productivity
·
More productivity = lower unit production cost =
SRAS
·
Lower productivity = higher unit production cost
= SRAS
Legal- institutional environment
·
taxes and subsidies
-taxes ($ to government) on
business increase per unit production cost = SRAS
-subsidies ( $ from government) to
business reduce per unit production cost = SRAS
Government regulation
-government regulation creates
cost compliance = SRAS
-deregulation reduces compliance
cost = SRAS
Full employment
·
Full employment occurs where AD intersects SRAS
and LRAS at the same point
Recessionary gap
·
Recessionary gap exists when equilibrium occurs
below full employment output
Inflationary gap
·
An inflationary gap exists when equilibrium occurs
beyond full employment output
Changes in AD
·
Change in consumption (c)
-c ^: AD : GDPr ^ & PL ^: U% v
-c v: AD
·
Change in gross private investment (Ig)
-Ig ^: AD
-Ig v: AD
·
Government spending (G)
- G ^ : AD
- G v : AD
·
Net exports (Xn)
-Xn ^ AD
-Xn v AD
Changes in SRAS
·
Input prices
- input prices v : SRAS
- input prices ^ : SRAS
·
Productivity
-productivity ^ : SRAS
-productivity v : SRAS
·
Legal-institutional environment
- deregulation : SRAS
- regulation : SRAS
Nominal wages- the
amount of money received by a worker per unit of time (how much you make)
Real wages- amount of goods and services that a
worker car purchase with their nominal wages (purchasing power of nominal
wages)
Sticky wages- nominal wage level that is set according to an
initial level and does not vary due to labor contracts or other restrictions.
Output- depends upon changes in the employment level.
Output depends upon changes in price and employment level output is independent
in changes in price level.
Keynasian
Range
Classical range
|
price
|
Wages
|
Employment level
|
implications
|
|
recession
|
fixed
|
fixed
|
flexible
|
||
Intermediate
|
flexible
|
fixed
|
flexible
|
||
inflation
|
flexible
|
flexible
|
fixed
|



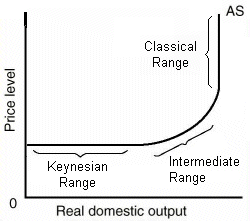
Hello Jocelyn, great blog I just want to elaborate a little bit on the Keynesian range; the Keynesian AS curve assumes that prices and wages are fixed until full employment is reached. Over the ‘Keynesian range’ there is spare capacity in the economy, the price level is stable, and real output can expand as a result of increases in AD without any inflationary pressure.
ReplyDelete