Unit 1 Macro
Economics
January 5, 2016
Macroeconomics- study of the
economy as a whole big picture. (inflation, wage, laws, and international
trade)
Microeconomics- study of the
individual or specific units of the economy. Supply and demand, market
structures, business organization)
Positive economics- attempt
to describe the world as it is. Very descriptive in nature (collects and
protects facts)
Normative economics- attempt
to prescribe how the world should be. (outta, should of) this is opinion based.
Needs- basic requirement for
survival (food, water, shelter, clothing)
Wants- desire but not necessary
Goods- tangible thing
something you can touch
(capitol
goods- items used in creation of other goods such as machinery and trucks
consumer
goods- goods that are intended for
final use by consumer)
services- work that is
perform fundamental problem that all societies face. Trying to satisfy
unlimited wants with limited resources.
Scarcity- most fundamental
problem that all societies face. Trying to satisfy unlimited wants with limited
resources.
Shortage- quantity demanded
is greater than supply
Factor
of production
1.
Land-natural
resource
2.
Labor- work
force
3.
Capitol- human
capitol, physical capitol
4.
Entrepreneurship-
innovative, risk- taker
Resources require to produce goods and services
Human capitol- knowledge, skills, abilities, talents, acquired through education or
experience
Physical capitol- tools, machines, factories, robots, trucks
January 6,2016
Trade-offs-
alternative that we give up whenever we choose one course of action over
another
Opportunity cost- next best alternative ex. Drink get the next best thing cos the place
ran out.
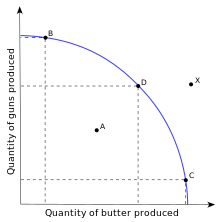
Production possibilities curve- graph that shows alternative ways to use an
economies resources.
4 assumptions of ppg
1.
Two goods
2.
Fixed resources
(land, labor, capitol, entrepreneurship)
3.
Fixed technology
4.
Full employment
of resources
Efficiency- uses resources in such a way as to maximize the
production of goods and services.
Allocative efficiency- the products being produced are the ones that the
society desires
Productive efficiency- products are being produced in the least costly way
and this will represent any point on the ppc or production possibility curve
Underutilization- using fewer resources than an economy is capable of using
3 types of movements within ppg
1.
Inside the ppc-
this occurs when resources are unemployed or underemployed
2.
Along the ppc-
going from B to C or from C to B on the curve
3.
Shifts the ppc-
so if there is an increase in the curve the shift would be D
January 7th
What causes the ppc/ppf to shift?
1.
Advances in
technology
2.
Change in
resources
3.
Change in labor
force
4.
Economic growth
5.
Natural
disasters/ war / famine
6.
More education
on training (human capitol)
January 11, 2016
Demand
Law of demand- the quantities that people are willing and able to
buy at various prices.
Law of demand- occurs when there is an inverse relationship
between price and quantity demanded.
A change in price causes a change in quantity demanded.
What causes a “change”
in demand?
1.
Change in buyers
taste (advertisement)
2.
Change in number
of buyers (population)
3.
Change in price
of related goods
4.
Change in income
5.
Change in
expectations-looking at the future.
Supply
Supply-
the quantities that producers/sellers are willing and able to produce at various prices.
The law of supply- there is a direct relationship between price and quantity supplied.
Change in price causes a “change in quantity supplied”
What causes a “change in supply”?
1.
Change in
expectations
2.
Change in
weather
3.
Change in number
of suppliers
4.
Change in cost
of production
5.
Change in taxes
or subsides
6.
Change in
technology
January 14, 2016
Elasticity of demand- measure of how consumes react to a change in price.
Elastic demand- it is demand that is very sensitive to a change in
price. E>1.
·
Product is not a
necessity.
·
Available
substitutes.
Inelastic demand- demand that is not very sensitive to a change in price. E<1
·
Product is a
necessity
·
Few or no
substitutes
Unit/ unitary elastic- E=1
Elastic demand (Ex. Soda, steaks, candy, fur coats)
Inelastic demand (Ex. Gas, insulin/ medicine, milk, salt, toothpaste)
Price elasticity demand- 3-step formula
|
ELASTIC
|
INELASTIC
|
|
soda
|
gas
|
|
steaks
|
salt
|
|
candy
|
milk
|
|
candy
|
Insulin/
medicine
|
|
Fur
coats
|
toothpaste
|
Step 1:
quantity (new quality-old quantity)
Old quantity
Step 2: price of
item (new price -old price)
Old price
Step 3: PED (%
change in quantity demanded)
% change in price
Cost of production
Total
revenue- the total amount of money a
firm receives from selling goods and services. PxQ=TR
Fixed
cost- a cost that does not change no
matter how much is produced.
Ex.(rent,
mortgage, salaries, insurance)
Variable
cost- a cost that rises or falls
depending upon how much is produced
Ex
(electricity)
Marginal
costs- the costs of producing one
more unit of a good
Formulas-
TFC+TVC=TC
AFC+AVC=ATC
TFC/Q=AFC
TVC/Q=AVC
TC/Q=ATC
TFC=AFC*Q
TVC=AVC*Q
MC=TC-ATC